MongoDB Database Structure
MongoDB Database Structure
MongoDB, a popular NoSQL database, utilizes a flexible
document-based structure to store data. Here's a breakdown of its key
components:
1. Databases:
- A
logical container for a set of collections.
- You
can have multiple databases within a single MongoDB instance.
- Databases
are typically named to reflect their purpose (e.g.,
"customer_db", "product_db").
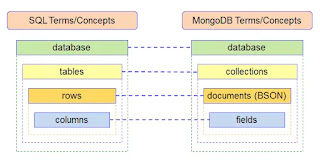
2. Collections:
- Analogous
to tables in relational databases.
- Store
a set of documents.
- Can
contain documents with varying structures within the same collection.
3. Documents:
- The
fundamental unit of data storage in MongoDB.
- Similar
to JSON objects, they consist of key-value pairs.
- Keys
are strings, and values can be of various data types:
- Strings
- Numbers
(integers, decimals)
- Booleans
- Arrays
- Embedded
documents (objects within a document)
- Dates
- Binary
data
Many of the components that go into the MongoDB data
structure have their counterparts in relational database management systems
based on the Structured Query Language (SQL).
Example:
JSON
{
"_id":
ObjectId("5f49c3d27007234567890abc"), // Unique identifier
"name": "John
Doe",
"age": 30,
"address":
{
"street":
"123 Main St",
"city": "Anytown",
"state":
"CA"
},
"hobbies":
["reading", "hiking", "coding"]
}
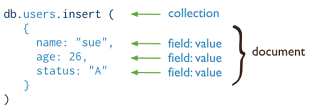
The document, which is comprised of field/value
pairs, is at the heart of the MongoDB data structure. Most interactions with
MongoDB occur at the document level.
A field can contain a single value,
multiple fields, or multiple elements.
A field can be one of these MongoDB data types:
|
Type |
Alias |
|
Double |
“double” |
|
String |
“string” |
|
Object |
“object” |
|
Array |
“array” |
|
Binary data |
“binData” |
|
Undefined |
“undefined” |
|
ObjectId |
“objectId” |
|
Boolean |
“bool” |
|
Date |
“date” |
|
Null |
“null” |
|
Regular Expression |
“regex” |
|
DBPointer |
“dbPointer” |
|
JavaScript |
“javascript” |
|
Symbol |
“symbol” |
|
JavaScript (with scope) |
“javascriptWithScope” |
|
32-bit integer |
“int” |
|
Timestamp |
“timestamp” |
|
64-bit integer |
“long” |
|
Decimal128 |
“decimal” |
|
Min key |
“minKey” |
|
Max key |
“maxKey” |
Key Characteristics:
- Schema-less:
You don't need to define a strict schema upfront. Documents within a
collection can have different fields.
- Dynamic:
The structure of documents can evolve over time as your application needs
change.
- Flexible:
Handles complex data structures easily due to the use of embedded
documents and arrays.
Visual Representation:
MongoDB database structure with databases, collections, and
documents
By understanding this structure, you can effectively model
and store your data in MongoDB, leveraging its flexibility and scalability for
various applications.
Code to connect MongoDB to Python and create a database
and a collection in MongoDB
import pymongo # Replace the connection string with your MongoDB connection string mongo_uri = "mongodb://username:password@localhost:27017/mydatabase" # Connect to MongoDB client = pymongo.MongoClient(mongo_uri) # Create or access a database db = client.get_database("mydatabase") # Create or access a collection collection = db.get_collection("mycollection") # Insert a document into the collection data_to_insert = { "name": "John Doe", "email": "john@example.com", "age": 30 } inserted_doc = collection.insert_one(data_to_insert) print(f"Inserted document ID: {inserted_doc.inserted_id}") # Close the MongoDB connection (optional, but recommended) client.close()
Query the MongoDB database using the find() method
import pymongo # Replace the connection string with your MongoDB connection string mongo_uri = "mongodb://username:password@localhost:27017/mydatabase" # Connect to MongoDB client = pymongo.MongoClient(mongo_uri) # Access the database and collection db = client.get_database("mydatabase") collection = db.get_collection("mycollection") # Define a query filter query_filter = {"age": {"$gte": 30}} # Use the find() method with the query filter cursor = collection.find(query_filter) # Iterate through the results and print them print("Documents with age greater than or equal to 30:") for document in cursor: print(document) # Close the MongoDB connection (optional, but recommended) client.close()
Labels: Collections, Database Structure, Document Database, MongoDB, NoSql, pymongo




0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home